Ephemeral Rivers in India: Meaning, Features & Examples
Advertisements
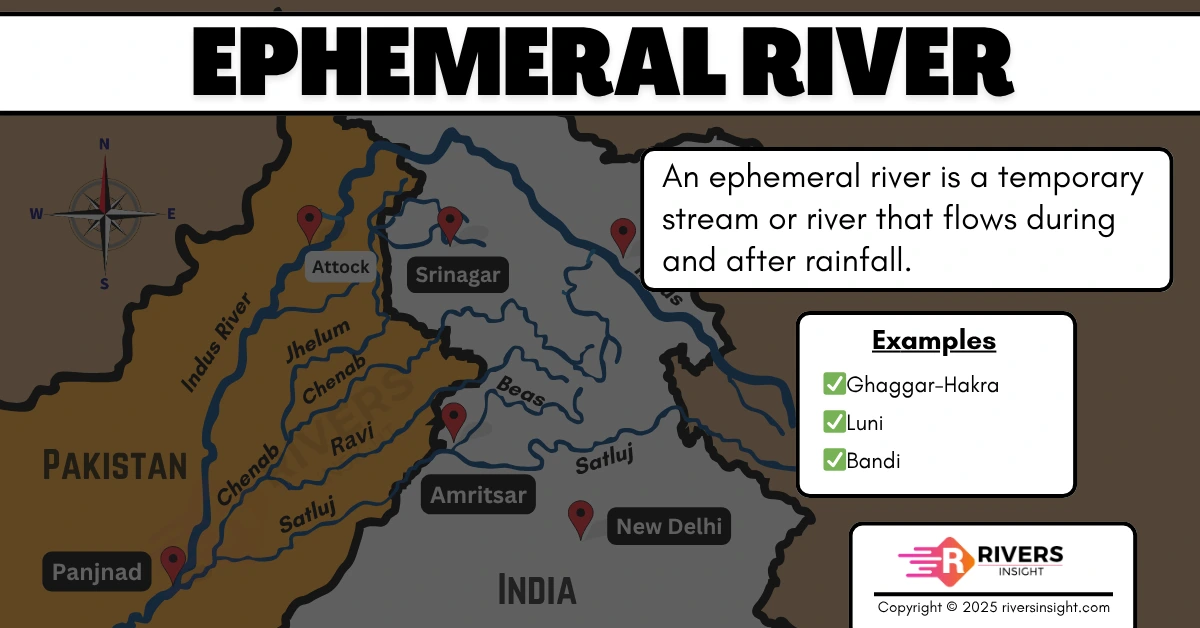
An ephemeral river is a type of river that flows only during periods of significant rainfall. Unlike perennial rivers that flow year-round, ephemeral rivers remain dry for most of the year and carry water only occasionally.
What is an Ephemeral River?
- Definition: An ephemeral river is a temporary stream or river that flows briefly during and after rainfall.
- Dry Beds: These rivers typically have dry riverbeds, known as wadis, nullahs, or ravines, depending on the region.
- Flow Duration: Flow may last from a few hours to a few days.
- Source of Water: Their water is primarily runoff from rain, not from groundwater or melting snow.
Characteristics of Ephemeral Rivers
- Rainfall-dependent: Flow only after heavy rain.
- Dry Most of the Year: Unlike seasonal rivers, they remain dry for extended periods.
- Common in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: Found in deserts and drylands.
- High Erosion Potential: Due to sudden water surges.
- No Base Flow: They don’t have a sustained water source like springs or glaciers.
Examples of Ephemeral Rivers in India
- Ghaggar-Hakra
- Luni River
- Bandi River
- Katni River
Difference Between Ephemeral and Perennial Rivers
| Feature | Ephemeral River | Perennial River |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Duration | Only during/after rainfall | All year round |
| Water Source | Rainfall runoff | Glaciers, springs, rainfall |
| Base Flow | Absent | Present |
| Common Region | Arid/semi-arid | Humid/sub-humid |
| Example (India) | Ghaggar-Hakra | Ganga, Brahmaputra |
📌 You can also explore our detailed article on Perennial Rivers and Rivers of Rajasthan for more context.