Ghaghara River (Karnali River): Origin, Map & Tributaries
The Ghaghara River, known as the Karnali River in Nepal and Mapcha Tsangpo in Tibet, is a major perennial river system in the Indian subcontinent. Originating from the Tibetan Plateau and flowing southward into the Ganges River, it traverses the territories of China, Nepal, and India.
Table of Contents
Origin of the Ghaghara River
The origin of the Ghaghara River is from the Mapchachungo Glacier in Tibet. In Nepal, it is known as the Karnali River and gains strength from two major Himalayan tributaries:
- Seti River (Right bank)
- Bheri River (Left bank)
Together, they form the Karnali system, which flows into India and becomes the Ghaghara.
Course of the Ghaghara/Karnali River
- In Tibet:
- Originates from glaciers in the Himalayas, notably near Lake Mansarovar.
- In Nepal:
- Flows southward through Humla, Mugu, Surkhet, and other remote districts.
- It is joined by tributaries such as the Seti and Bheri Rivers.
- The river flows through the Siwalik Hills, splitting into two branches — Geruwa (left) and Kauralia (right) — near Chisapani.
- In India:
- The branches reunite before entering India, where it is called the Ghaghara River.
- It merges with the Sharda River at Brahmaghat.
- Flows through Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, finally joining the Ganges River at Revelganj in Bihar.
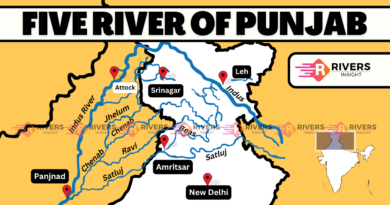
Ghaghara River Map Overview
The river begins in the Tibetan Himalayas and ends in the Ganga River at Revelganj, Bihar. Here is a map of the Karnali River and the Ghaghara River:

Length and Drainage Basin
- Total Length: Approx. 1,080 km
- 507 km in Nepal
- 573 km in India
- Catchment Area: 127,950 square kilometers
- About 55% lies in Nepal
- Around 45% lies in India
Major Tributaries of the Ghaghara River
In Nepal:
- Seti River (Right bank)
- Bheri River (Left bank)
- Tila and Kawadi Rivers
In India:
Left Bank Tributaries:
- Kuwana River
- Rapti River
- Chhoti Gandak (Groundwater-fed; joins near Siwan, Bihar)
- Khanua River
Right Bank Tributaries:
- Seti River (Indian side)
- Sarda River (Also known as Mahakali River)
- Budhi Ganga
- Dahawar River
Major Dams and Hydropower Projects
- Karnali Chisapani Hydropower Project (Nepal)
- Upper Karnali Hydropower Project (Nepal)
- Girijapuri Barrage (India)
Flood Situation Near Ghaghara River
The flood situation near the Ghaghara River becomes critical during the monsoon months (July–September) due to:
- Excess rainfall in the Himalayas
- Rapid snowmelt
- Poor drainage infrastructure in low-lying Indian districts
Affected regions:
- Eastern Uttar Pradesh: Bahraich, Balrampur, Gonda
- Northern Bihar: Saran, Gopalganj, Siwan
Floods cause riverbank erosion, agricultural loss, and displacement, and pose a major challenge for disaster management authorities.
Environmental Importance
- Bardia National Park (Nepal): Home to endangered species like the South Asian river dolphin, gharial, mugger crocodile, Asian elephants, and golden mahseer.
- Katarniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary (India): A protected zone in Uttar Pradesh, important for migratory birds and riparian ecosystems.
Religious & Historical Significance
- The Sarayu River, which forms part of the Ghaghara system in India, holds religious importance in Hindu mythology.
- The city of Ayodhya, believed to be the birthplace of Lord Rama, is located on its banks.
- The river is also historically important, as key battles (such as that between Amin Khan Aitigin and Tughral Tughan Khan) have taken place along its course.