Bhavani River: Map, Origin, Tributaries & Drainage Basin
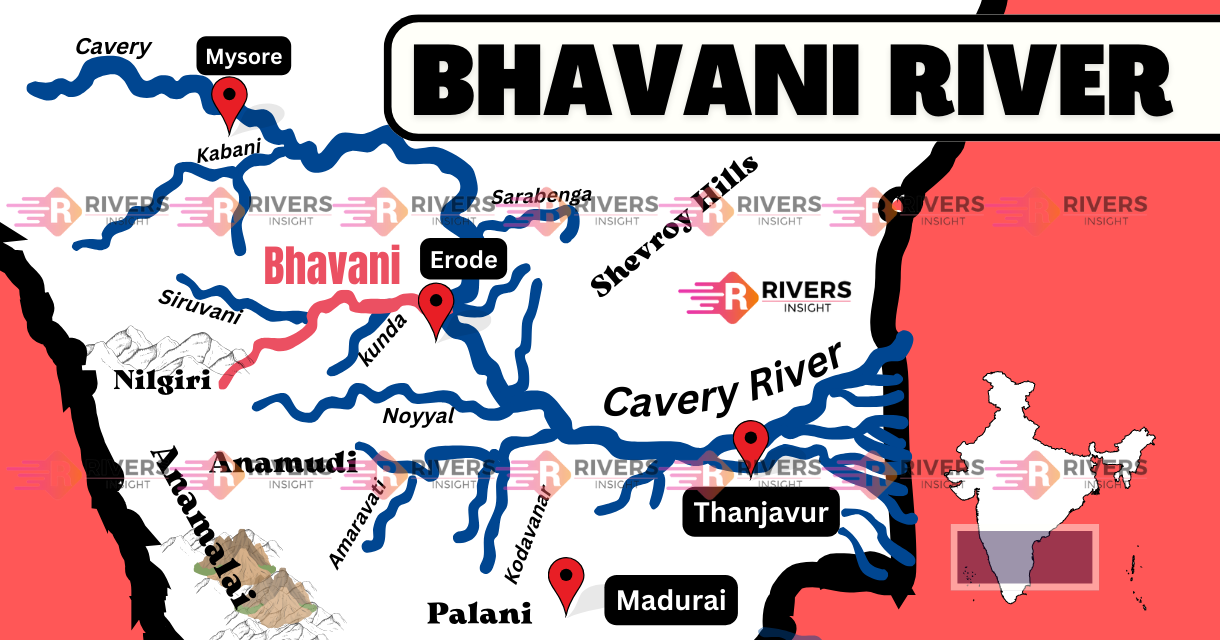
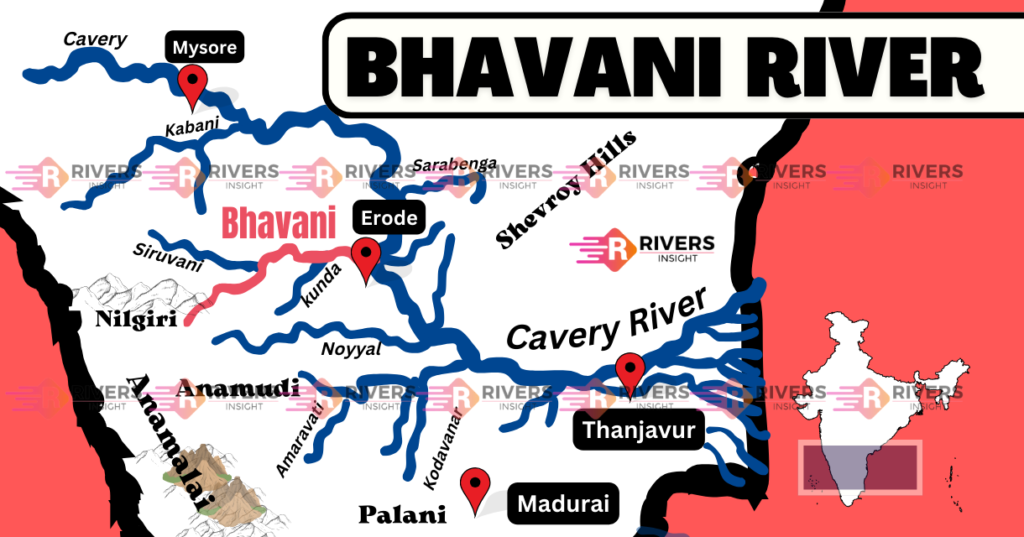
Bhavani River is a major tributary of the Cauvery River and is the second-largest river in Tamil Nadu, India. It has a total length of 217 kilometers and flows through the states of Kerala and Tamil Nadu. Originating in the Nilgiris of the Western Ghats, the perennial river flows eastward and eventually drains into the Cauvery River Basin.
| Length | 217 km |
| Starting Point | Nilgiri Hills, Tamil Nadu |
| Ends at | Cauvery River at Bahvani |
| Catchment | 6,200 sq. km. |
| States | Kerala and Tamil Nadu |
Table of Contents
Origin and Course of Bhavani River
Bhavani River originates from the Western Ghats in the Nilgiri Hills, located in the Tiruppur district of Tamil Nadu. The river emerges from the Bhavani Lake, at an elevation of about 2,165 meters (7,100 feet) above sea level. From there, it travels eastward towards the plains of Tamil Nadu.
Course of the Bhavani River:
The river flows through the Coimbatore and Erode districts of Tamil Nadu, with several important towns such as Mukkali, Mettupalayam, and Bhavani located along its banks.
After its origin, the Bhavani turns northeast and flows through the Attappady Plateau, spanning around 25 kilometers before crossing the interstate border between Kerala and Tamil Nadu. The river flows through the Nilgiris, and its course includes major towns like:
- Sathyamangalam
- Gobichettipalayam
- Aavudaiaaparai
A prominent confluence occurs at Koodappatti, where the river is joined by the Siruvani River from the Coimbatore district and the Kodungarapallam River from the Kerala-Tamil Nadu border. The river then continues its eastward journey, passing through Mettupalayam, where the Coonoor River joins it.
Finally, the river merges with the Cauvery River in the town of Bhavani, at a location known as Bhavani Sangameshwarar Temple, a significant pilgrimage site for Hindus.
Drainage Basin
The drainage basin of the Bhavani River spans approximately 6,200 square kilometers, covering parts of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Karnataka:
- Tamil Nadu: 87% of the basin area
- Kerala: 9% of the basin area
- Karnataka: 4% of the basin area
Map of Bhavani River – Start to End
Tributaries of the Bhavani River
Bhavani River receives water from several important tributaries, which help to sustain its flow and support the agricultural needs of the region. Some of the most significant tributaries include:
- West and East Varagar Rivers: These are the largest tributaries of the Bhavani River, originating from the Nilgiris and contributing a substantial amount of water to the river.
- Kunda River: The Kunda River, coming from the north, joins the Bhavani at Athikadavu in western Tamil Nadu, enriching its flow.
- Siruvani River: The Siruvani River, which originates from Kerala, flows into the Bhavani at Koodappatti. It is an important water source for the Coimbatore region.
- Kodungarapallam River: Another tributary that joins the Bhavani River in the Kerala-Tamil Nadu border region.
- Coonoor River: The Coonoor River, which originates in Coonoor, joins the Bhavani near Mettupalayam, contributing further to its flow.
Dams
There are two major dams on the Bhavani River:
- Bhavani Sagar Dam
- Kodiveri Dam
Did you find this article informative? Share it with your friends and family to spread awareness about the Bhavani River. If you have any questions or thoughts, leave a comment below!