Bhadar River of Gujarat: Map the Course
Bhadar River is one of the most significant rivers of Gujarat, particularly in the Kathiawar (Saurashtra) Peninsula. Originating from the hills of Rajkot district, it flows through several important towns before eventually merging with the Arabian Sea.
Table of Contents
Origin and Course of Bhadar River
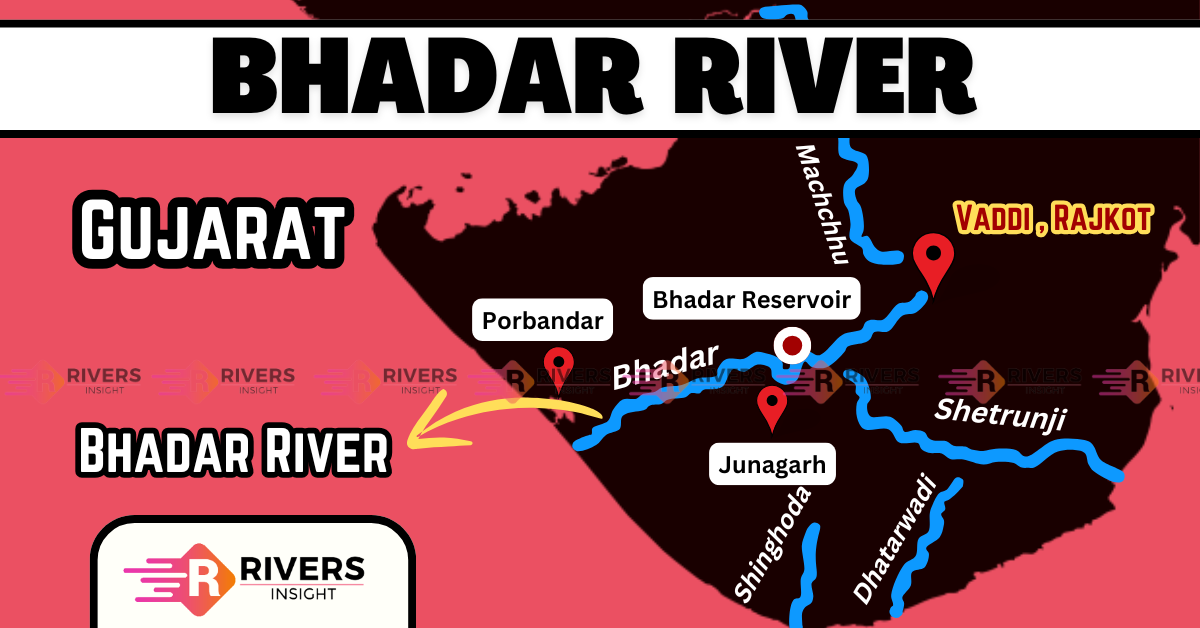
The Bhadar River originates near Vaddi (Aniali Village), about 26 km northwest of Jasdan in Rajkot district, at an elevation of 261 meters above sea level. From its source, the river initially flows southward until it reaches Jasdan.
After this point, it changes course towards the southwest and continues in that direction until it passes through Jetpur. Eventually, the river turns westward and continues its journey until it meets the Arabian Sea at Naviobandar in Porbandar.
Length and Drainage Basin
- Total length: 198 km
- Drainage area:7,094 sq. km
- Hilly region: 706 sq. km
- Remaining area: Mostly plains of Saurashtra
Bhadar River Basin covers about 1/7th of the total area of Saurashtra, making it a vital hydrological system in the region.
Geographical Coordinates
- Latitude: 21°25′ to 22°10′ N
- Longitude: 69°45′ to 71°20′ E
Tributaries of the Bhadar River
Bhadar River is fed by nine major tributaries, classified into right-bank and left-bank tributaries. The right-bank tributaries contribute more significantly to the river’s flow.
Right-Bank Tributaries (Larger Drainage Area)
- Gandali River
- Chapparwadi River
- Phopal River
- Utawali River
- Moj River
- Venu River
Left-Bank Tributaries
- Vasavadi River
- Surwa River
- Galolio River
Important Dam
Bhadar River has several dams and reservoirs constructed for irrigation, drinking water supply, and flood control. The Bhadar-1 Dam is a major project, while the Bhadar-2 Dam is currently under construction to improve water storage and irrigation.
Additionally, several smaller dams and reservoirs have been built on the river and its tributaries, including:
- Fofal Dam
- Chhaparvadi-1 Dam
- Gondli Dam
- Survo Dam
- Moj Dam
- Venu-2 Dam
- Sankroli Dam
These dams play a crucial role in water conservation, groundwater recharge, flood control, and agricultural irrigation, ensuring a sustainable water supply for Saurashtra.