Kaimur Hills and Maikal Hills in India | Map & Facts
Advertisements
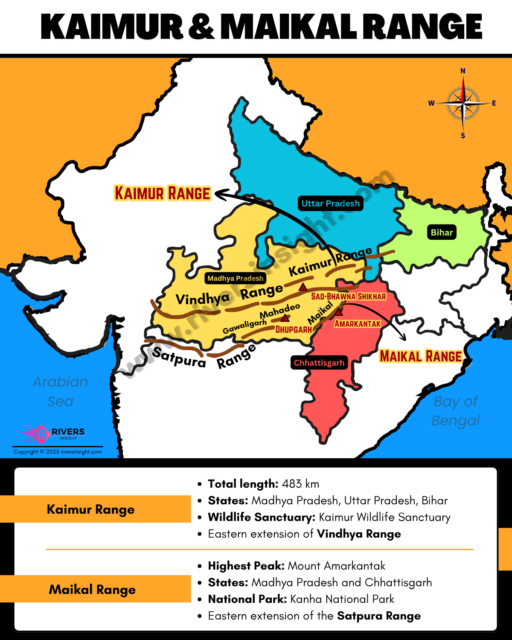
Kaimur Hills and Maikal Hills are two significant hill ranges of Central India. Kaimur Hills form the eastern extension of the Vindhya Range, while Maikal Hills represent the eastern extension of the Satpura Range. This combined article covers their location, geographical features, wildlife areas, and map-based clarity to help users understand both ranges easily.
1. Kaimur Hills
Kaimur Hills form the eastern extension of the Vindhya Range, running across central–eastern India. They stretch from Jabalpur (Madhya Pradesh) to Sasaram (Bihar) with a long escarpment overlooking the plains.
- Total length: ~483 km
- States: Madhya Pradesh → Uttar Pradesh (border) → Bihar
- Rivers: Durgavati, Son, Karamnasa, and Chandraprabha
- Bounded by Son River to the south and Ganga plains to the north
- Major waterfalls: Telhar Kund, Karkatgarh, Tutrahi (Tutla Bhavani), Durgavati Falls, Banshi Kund, Budhua–Dhansa falls
- Wildlife Sanctuary: Kaimur Wildlife Sanctuary
- Tribes: Kharwar, Chero, Oraon
2. Maikal Hills
Maikal Hills lie at the junction of Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. They form the eastern extension of the Satpura Range, centered around Amarkantak.
- Key region: Amarkantak Plateau
- Total length: ~500 km
- Acts as divide between Narmada Basin and Mahanadi Basin
- Elevation: 300–1000 m
- States: Madhya Pradesh & Chhattisgarh
- Highest Peak: Mount Amarkantak
- Natural divide between Narmada (west-flowing) and Mahanadi (east-flowing) basins
- Origin of major rivers: Narmada, Son, Johila, and Mahanadi
- National Park: Kanha National Part and Achanakmar Wildlife Sanctuary
- Tribes: Baiga, and Gond