Kameng River of Arunachal Pradesh: Map & Origin
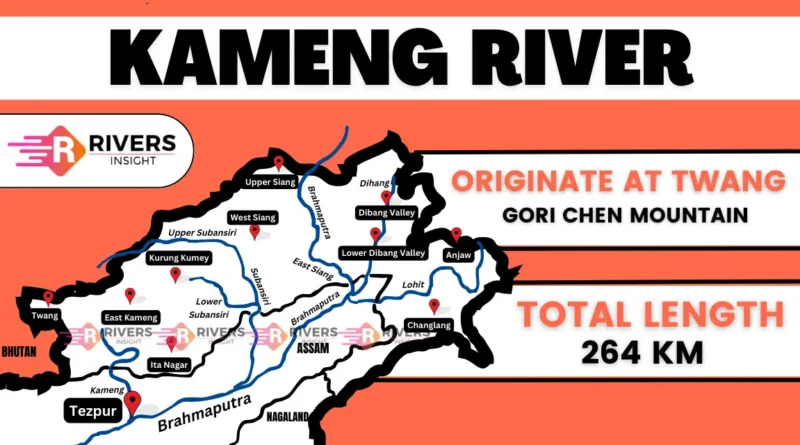
The Kameng River, also known as the Jia Bharali River, originates from a glacial lake below the snow-capped Gori Chen Mountain on the India-Tibet border in the Tawang district. Spanning approximately 264 kilometers, it is a vital waterway in Northeast India.
It flows entirely within India, passing through the Bhalukpong Circle of West Kameng District in Arunachal Pradesh and Sonitpur District in Assam. As it reaches its lower stretches, the river transforms into a braided channel and merges with the Brahmaputra at Tezpur, just east of the Kolia Bhomora Setu bridge.
Table of Contents
Tributaries
- Tippi River
- Tenga River
- Bichom River
- Dirang Chu
Important Hills from Which It Passes
The Kameng River flows past several important hills that define its geographical and ecological context. To the east of the river lie the Dafla Hills, known for their dense forests and biodiversity. On the western side, the Aka Hills rise prominently, providing a rich habitat for various species of flora and fauna. These hills are geographical landmarks and play a crucial role in the local climate and ecology.
Tribes Around Kameng River
The Kameng River region in Arunachal Pradesh is culturally rich and diverse, home to various indigenous tribes. Here is a list of some major tribes found in the area:
- Monpa: Known for their distinctive culture and Tibetan Buddhist heritage, the Monpas primarily inhabit the Tawang district and parts of West Kameng district.
- Aka (Hrusso): The Aka, also known as Hrusso, are indigenous to the hilly regions of West Kameng district. They have a unique cultural identity and traditional knowledge of the forest ecosystems.
- Sherdukpen: The Sherdukpen tribe resides in the hills of the West Kameng district. They have a rich cultural heritage, including unique festivals, rituals, and craftsmanship.
- Nyishi: One of the largest tribes in Arunachal Pradesh, the Nyishi people predominantly inhabit the East Kameng district. They are known for their traditional agricultural practices and vibrant festivals.
- Adi (Galo): The Adi, also known as Galo, are one of the major tribes in Arunachal Pradesh. They reside in the Upper Siang, West Siang, and East Siang districts, including parts of the Kameng River region.
- Tagin: The Tagin tribe inhabits the Upper Subansiri district and parts of the West Kameng district. They have a rich cultural heritage, including traditional dances, rituals, and handicrafts.
- Miji: The Miji tribe resides in the West Kameng district and other adjoining areas. They have a distinct cultural identity and are known for their traditional agricultural practices.
- Bugun: The Bugun tribe inhabits the Eaglenest Wildlife Sanctuary area near the Kameng River. They are known for their unique cultural practices and conservation efforts.
- Puroik (Sulung): Also known as Sulung, the Puroik tribe primarily inhabits the lower regions of the West Kameng and East Kameng districts. They have a rich oral tradition and cultural heritage.
- Hill Miri: The Hill Miri tribe resides in the hills of the West Kameng district. Their unique cultural identity includes traditional dances, songs, and rituals.
These tribes contribute to the cultural diversity and heritage of the Kameng River region, each with its distinct traditions, languages, and way of life.