Nubra River: Key Facts and Map
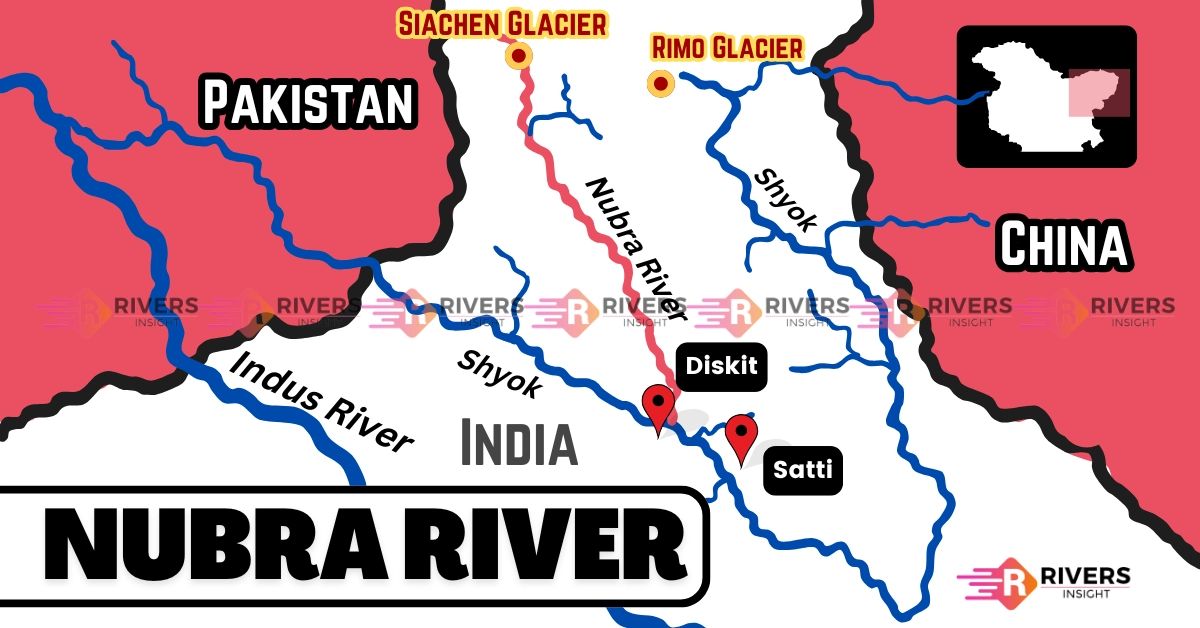
Nubra River is a glacial tributary of the Shyok River, located in the northern Indian subcontinent, within the Union Territory of Ladakh. It originates from the Siachen and Terong glaciers and flows through the high-altitude Nubra Valley. As part of the larger Indus River system, the Nubra River ultimately contributes to the flow of the Indus River via the Shyok.
Key Facts about the Nubra River
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Country | India |
| Region | Ladakh |
| Source | Siachen Glacier, Terong Glacier |
| Length | ~90 km |
| Confluence | Joins Shyok River near Diskit village |
| Tributary Type | Right-bank tributary of Shyok River |
| Flow Direction | Southeast |
| Mountain Ranges | Between Karakoram and Saltoro Mountains |
| Historical Name | Yarma Tsangpo (in old Tibetan maps) |
Origin and Formation of Nubra River
Nubra River originates from the Siachen Glacier, one of the largest glaciers in the Karakoram range. The river begins as glacial meltwater emerging from ice caves at the glacier’s terminus. This meltwater forms the initial stream, which combines with flows from Terong Glacier and several smaller glaciers in the region.
Glacial Sources:
- Siachen Glacier (primary)
- Terong Glacier
- Other minor glaciers in the Karakoram Range
Course of the River
After its formation, the Nubra River flows in a southeasterly direction, running between the Karakoram and Saltoro mountain ranges. It covers a total distance of approximately 90 km (56 miles).
The river ultimately merges with the Shyok River near the village of Diskit in the Nubra Valley. The Shyok River then continues its course and joins the Indus River at Keris, east of Skardu (in present-day Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan).
Hydrological and Geological Significance
1. Seasonal Variation
The Nubra River exhibits strong seasonal variation. Its flow peaks between June and September, when glacial melt is at its maximum due to higher summer temperatures. This results in:
- Increased discharge volume
- Higher sediment load transported downstream
2. Quaternary Geology
The Nubra River plays a significant role in the deposition of Quaternary sediments. These sediments are of considerable interest to researchers studying:
- Past climatic conditions
- Glacial-interglacial cycles
- Tectonic evolution of the Ladakh region
Strategic and Geopolitical Importance
- The Siachen Glacier, the source of the Nubra River, is known as the world’s highest battlefield, where India and Pakistan have maintained military presence for decades.
- The Nubra Valley, through which the river flows, is a strategic corridor connecting India’s northern military outposts.
- Control of the Nubra-Shyok-Indus river system is vital for water security and border infrastructure in this sensitive region.
Conclusion
The Nubra River is a short but highly significant river in the trans-Himalayan region of Ladakh. With origins in the Siachen and Terong glaciers, it is not only vital for the local hydrology and agriculture but also plays a crucial role in geological research and border security. Understanding its geography, flow patterns, and glacial sources provides insight into the complex natural systems of the Himalayan region.