Shyok River: Map, Origin & Tributaries
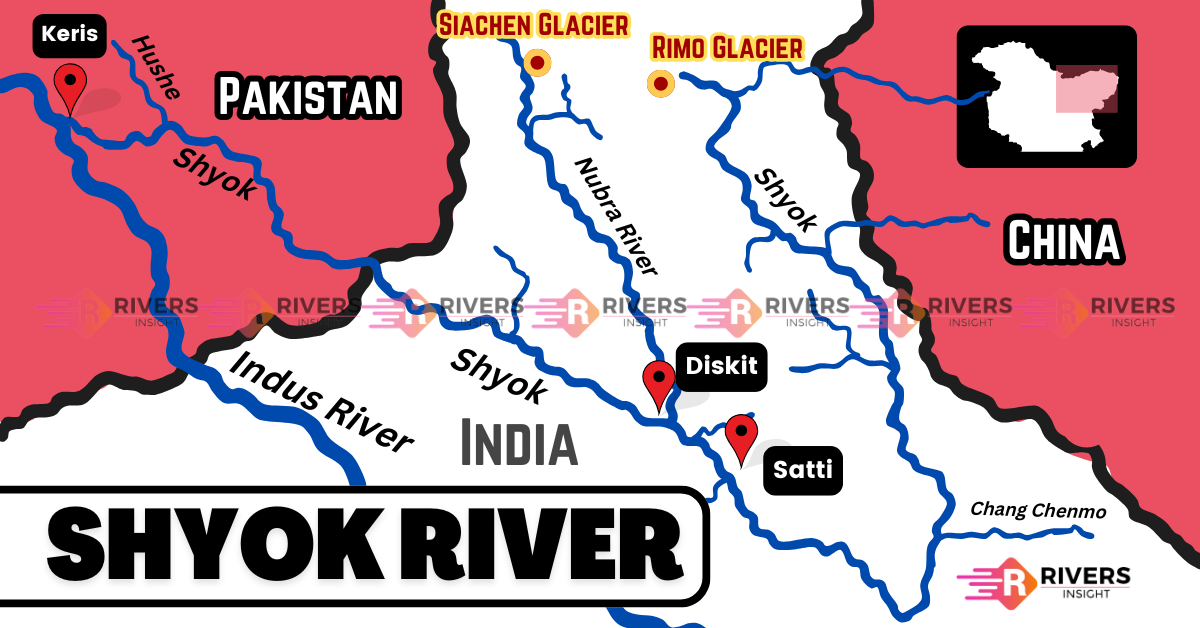
Shyok River is a major river in the Ladakh region of northern India and forms a significant part of the Indus River system. It originates from the Rimo Glacier, one of the tongues of the Siachen Glacier. It flows for approximately 550 kilometers along the Karakoram Range before merging with the Indus River in Gilgit-Baltistan. One of its key tributaries is the Nubra River, which joins from the right near the village of Diskit.
Furthermore, the origin of the Shyok River is located near the Siachen Glacier, a site that is the highest battlefield in the world.
Table of Contents
Origin and Source
- Primary Source: Rimo Glacier (a part of the Siachen Glacier system)
- Location of Source: Eastern Karakoram Range, Ladakh
- Approximate Elevation at Source: ~5,000 meters (16,400 feet)
The name “Shyok” is derived from a Tibetan word meaning “river of death,” likely due to its unpredictable flow patterns and dangerous terrain.
Course and Geography
The Shyok River flows southeastward from its glacial source, then takes a sharp turn northwest through the Nubra Valley, running parallel to the Karakoram Range.
Key Points Along the River:
- Confluence with Nubra River: Near Diskit in the Nubra Valley
- Flows through Villages: Durbuk, Tangtse, Turtuk
- Joins Indus River: Near Keris, east of Skardu (in Gilgit-Baltistan)
Tributaries of the Shyok River
The Shyok River has both left-bank and right-bank tributaries that contribute to its flow and hydrological importance, especially during summer months.
Left-Bank Tributaries:
- Chip Chap River
- Galwan River
- Chang Chenmo River
Right-Bank Tributaries:
- Nubra River
- Hushe River
Each of these rivers originates in high-altitude glacial or snow-fed zones, bringing in large volumes of sediment and meltwater during the warmer months (June to September).
Importance
- Strategic Access: The Shyok Valley offers vital routes to key passes in the Karakoram, including the Karakoram Pass, making it crucial for defense logistics.
- Local Livelihood: Despite harsh terrain, the river supports limited agriculture, livestock, and water supply for remote communities.
- Tourism Potential: Its dramatic landscapes attract adventure tourists for trekking, camping, and exploration.
- Geopolitical Significance: Located near the Line of Actual Control (LAC), the valley holds importance for border security and military operations.
Conclusion
Shyok River is not only a key geographical feature in Ladakh but also an essential link in the Indus River system. With critical tributaries like the Nubra River, Galwan River, and Chang Chenmo River, it holds environmental, strategic, and hydrological significance. Originating from near the highest battlefield in the world, this river remains central to both natural and human dynamics in the region.