Betwa River – Origin, Route, Tributaries & Map
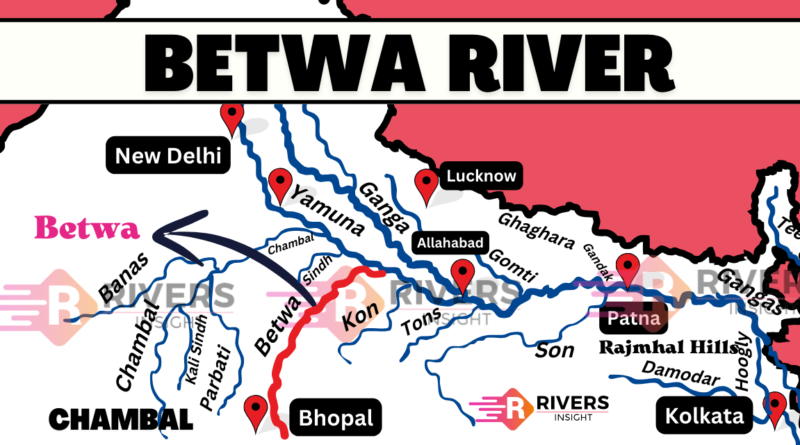
The Betwa River is a right-bank tributary of the Yamuna River. It flows through central India and holds both historical and ecological importance. It has been mentioned in the Mahabharata and once supported the Chedi Kingdom, whose capital Suktimati stood on its banks.
| Feature | Detail |
|---|---|
| Origin | Jhirri Village, Sehore (Madhya Pradesh) |
| States | Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh |
| Total Length | Approx. 590 km |
| End Point | Confluence with Yamuna at Hamirpur |
| Major Dams | Rajghat, Paricha, Matatila |
| Longest Tributary | Halali River (32 km) |
| Basin Size | Around 48,900 sq. km |
Table of Contents
Origin of Betwa River
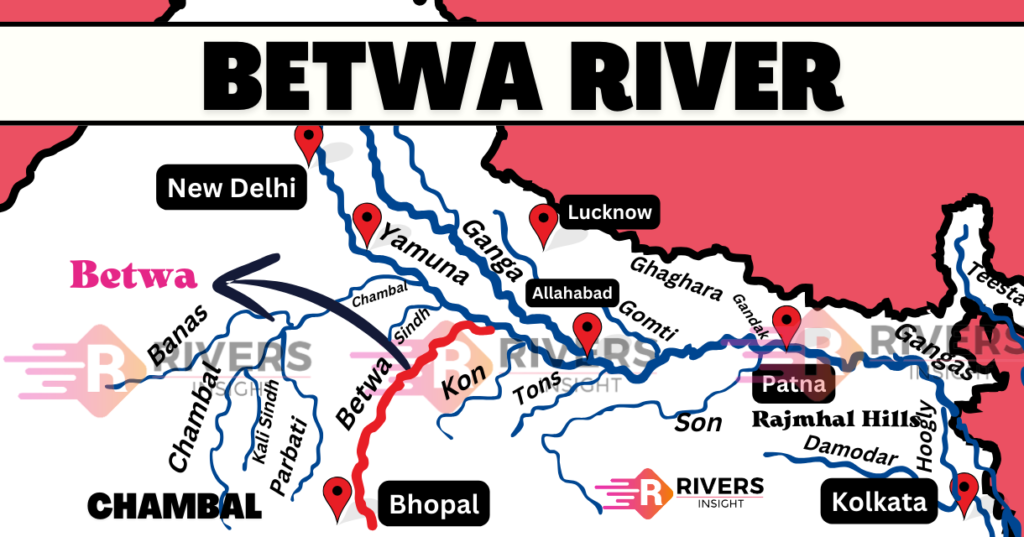
The Betwa River originates from Jhirri village in Sehore district, near Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh. It begins at an elevation of around 460 metres in the Vindhya hills. The river flows in a northeast direction, passing several districts before joining the Yamuna.
States and Districts Covered
The river flows through two Indian states:
- Madhya Pradesh
- Uttar Pradesh
Important districts along its course:
- Bhopal
- Vidisha
- Orchha
- Jhansi
- Hamirpur
Betwa River Map & Course
The total length of Betwa River is about 590 kilometres. It flows through rugged terrains and plains before joining the Yamuna near Hamirpur in Uttar Pradesh. A map of the river shows its journey from the Vindhya Range to the Yamuna confluence.
Tributaries of Betwa River
The Betwa River basin includes 14 tributaries. Among these, 11 are located entirely within Madhya Pradesh and 3 are shared with Uttar Pradesh.
Important tributaries are:
- Halali River – the longest tributary (about 32 km in length)
- Dhasan River – another important tributary
Major Dams
Several dams are built on the river for irrigation and power generation:
- Rajghat Dam
- Paricha Dam
- Matatila Dam
Betwa River Board (BRB)
The Betwa River Board was formed under the Betwa River Board Act, 1976. It oversees joint projects between Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh, mainly focused on dam construction and water management.
Where Does Betwa Meet the Yamuna?
The Betwa River joins the Yamuna near Hamirpur in Uttar Pradesh. This confluence point plays a role in the larger Ganga River system, as the Yamuna itself is a tributary of the Ganga.