Gandak River & Burhi Gandak: Map & Key Facts
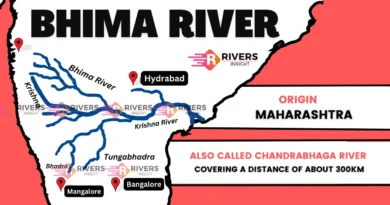
Gandak River is one of the major rivers of North India and a significant left-bank tributary of the Ganga River. It originates in the Himalayas of Nepal and enters India near Valmikinagar in Bihar. The river is also known as the Gandaki or Narayani River in Nepal.
It has a total length of about 630 kilometers, out of which 185 kilometers lie in Nepal and around 445 kilometers in India. The river travels through several districts of north Bihar before meeting the Ganga near Hajipur.
Table of Contents
Origin and Course of Gandak River
Gandak River originates north of the Dhaulagiri range in Tibet, close to the Nepal border. It is formed by the union of the Kali and Trisuli Rivers, which rise in the Great Himalayas of Nepal. From their meeting point till the Indian border, the river is known as the Narayani in Nepal.
It enters India near Valmikinagar in Bihar and briefly touches Uttar Pradesh, forming a small stretch of boundary. After this, the river flows mainly through Bihar, covering districts like West Champaran, East Champaran, Gopalganj, and Saran.
The Gandak finally joins the Ganga River opposite Patna, near Hajipur in Vaishali district, Bihar.
Drainage Basin
Gandak River has a large drainage basin that spreads across both Nepal and India. In Nepal, it covers a major part of the Gandaki Province. The total catchment area is about 46,300 square kilometers, out of which nearly 7,620 square kilometers fall in India.
The basin is bounded by the Himalayas to the north and the Ganga River to the south. On the sides, it lies between the Kosi basin in the east and the Karnali (Ghaghara) basin in the west.
Key Basin Facts:
- Major coverage: Nepal and northern Bihar
- Highest point: Dhaulagiri in Nepal
- Includes around 1,710 glaciers and over 300 lakes in the upper basin
Is Burhi Gandak the Same as Gandak River?
No, the Burhi Gandak River is a separate river system, though it flows close to the Gandak River in northern Bihar. The similar name often causes confusion, but both rivers have different sources and courses.
The Burhi Gandak starts from the Chautarwa Chaur near Bisambharpur in West Champaran. It flows through districts like Muzaffarpur and Samastipur, and finally joins the Ganga near Khagaria.
Unlike the Gandak, which carries glacier-fed Himalayan water, the Burhi Gandak is a rainfed river, more prone to seasonal flooding. Though they pass through the same region, the two rivers do not directly connect.
Tributaries
- Trisuli
- Bari
- Mayangadi
- Panchanad
- Daraudi
- Seti Gandaki
- Sarhad
Gandak Barrage
The most important structure on the Gandak River is the Gandak Barrage, located at Valmikinagar in West Champaran district, Bihar. It was built to control floods and provide irrigation water to the plains of Bihar and eastern Uttar Pradesh.
The barrage diverts water into two main canals:
- Western Gandak Canal – supplies water to Uttar Pradesh
- Eastern Gandak Canal – serves districts in Bihar
Additional Facts about the Gandak River
- The basin includes three peaks over 8,000 m: Dhaulagiri, Manaslu, and Annapurna Massif.
- Dhaulagiri is the highest point in the Gandak basin.
- Valmiki National Park and Tiger Reserve lies along the river in Bihar.
- On its banks are two national parks: Chitwan (Nepal) and Valmikinagar (India).
- Declared as National Waterway 37 from Bhaisalotan Barrage to Hajipur.
- The riverbed in Nepal contains Shaligrams, considered sacred in Hinduism.
- Muktinath in Mustang is a well-known site for Shaligram stones.
- Gandaki River is mentioned in the Mahabharata.
If you’re looking to understand more rivers in the region—like Kosi, Bagmati, or Ghaghara—we’ve covered them separately. And if you feel something here needs to be added or corrected, we’re always open to helpful suggestions.
Thank You!