Ramganga River with Map
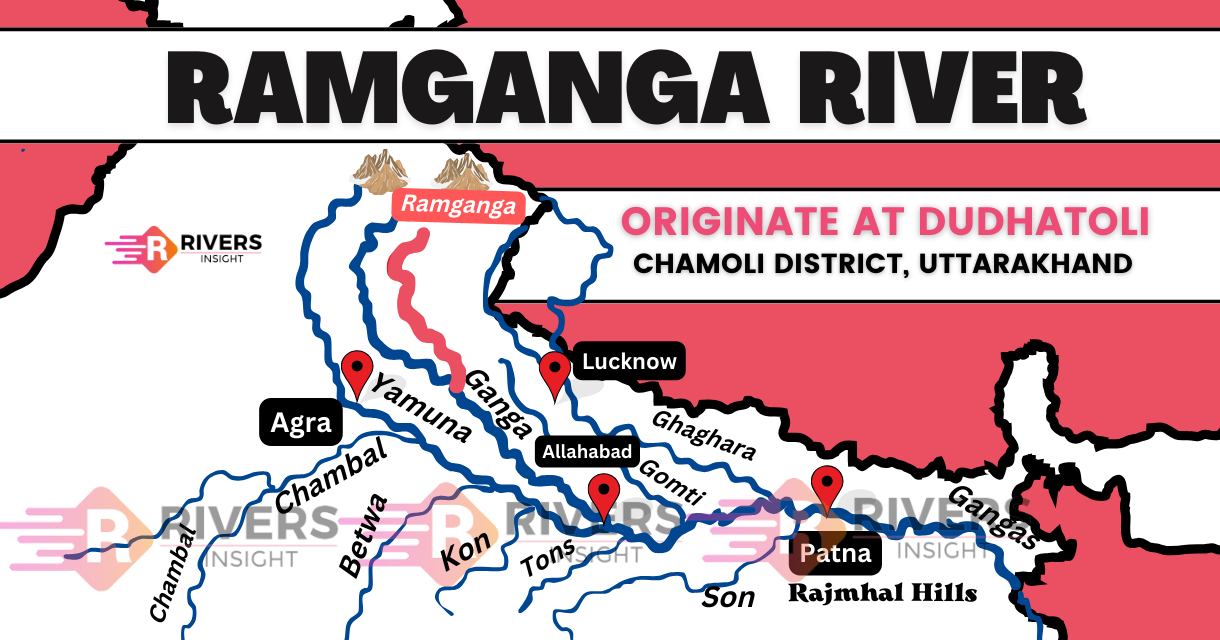
Ramganga River is a major tributary of the Ganga River in northern India, and it is interesting to note that it is divided into two main branches, specifically the Ramganga West River and the Ramganga East River. Meanwhile, both rivers have their origins in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, which is a region renowned for its natural beauty and rich biodiversity.
Table of Contents
Ramganga West River
The Ramganga West River originates in the Pauri Garhwal district of Uttarakhand, specifically in the Doodhatoli ranges, atfo, Chaukhutia, Bhagoti, Masi, and Bhikyasen. Eventually, it merges with the sacred Ganges River near Ibrahimpur in Uttar Pradesh. Moreover, The river has a drainage basin of around 30,641 square kilometers.
Cities Along Ramganga
The Ramganga West River is also home to several cities, including
- Moradabad
- Bareilly, Badaun
- Shahjahanpur
- Hardoi
Development of Ramganga West River
The Ramganga West River was developed through the Ramganga Multipurpose Project. A key part of this project is the Ramganga Dam, built between 1961 and 1974 near Kalagarh in Pauri Garhwal district. The dam is 128 meters high and 715 meters long.
The dam has a power station that generates 198 MW of electricity. It also supplies water to irrigate around 57,500 hectares of farmland, helping to control floods in the area. The dam has played a crucial role in the region’s development and continues to support the local community.
Ramganga East River
The Ramganga East River originates in the Pithoragarh district of Uttarakhand from the Namik Glacier and flows towards the east. The river is joined by several small and big rivers before merging with the Sarju River at Rameshwar near the Ghat of Pithoragarh. The Sarju River eventually merges with the Kali (Sharda) River.