Rapti River: Map and Origin | Floods
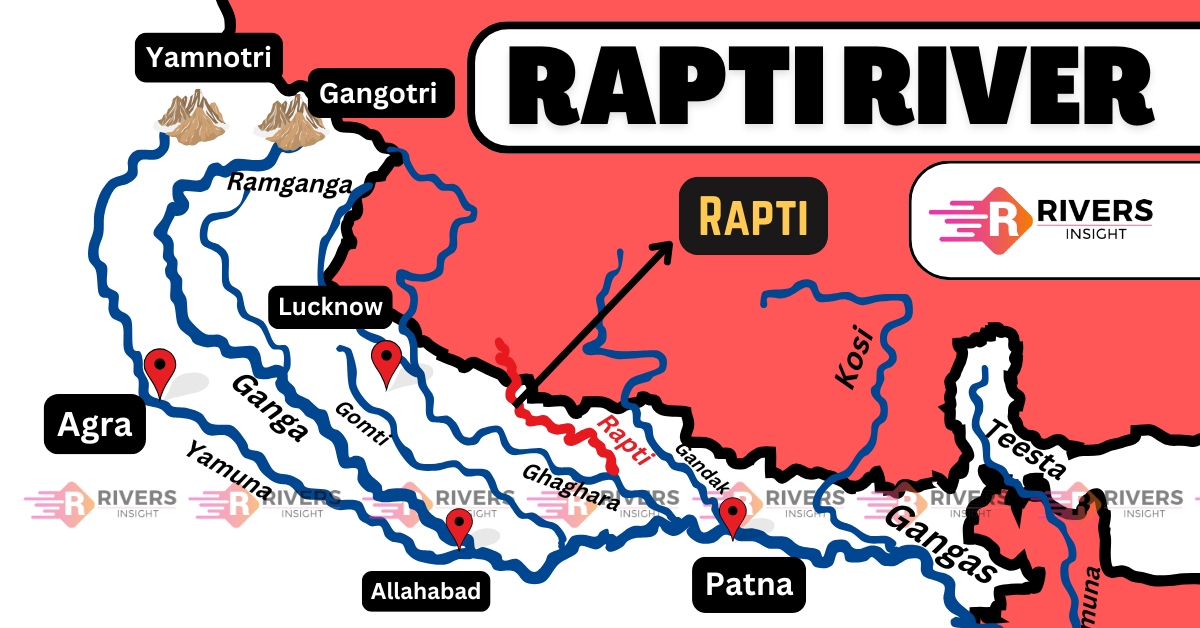
The Rapti River is a significant left-bank tributary of the Ghaghara River, flowing through Nepal and Uttar Pradesh, India. Historically known as Achiravati, Airavati, or Aciravati, it has deep cultural and religious importance, particularly in Buddhism and Jainism.
The river originates in the Middle Himalayas of Nepal and flows southward through the Terai region before joining the Ghaghara River, which ultimately merges with the Ganga River.
Table of Contents
Historical and Religious Significance
Ancient Names and References
- Achiravati, Airavati, Aciravati – Names in ancient Indian texts.
- A-chi-lo – Mentioned by Chinese traveler Xuanzang.
- Eravai or Iravati – Referenced in Jain scriptures.
Connection to Buddhism and Jainism
The Rapti River played a crucial role in ancient Indian civilizations. The city of Shravasti, a major center of Buddhist and Jain traditions, was located on its western bank. Gautama Buddha is believed to have spent many rainy seasons in Shravasti, preaching his teachings near the river.
In Jain literature, the river is mentioned in Kalpasutra, further reinforcing its religious significance.
Mentions in Historical Texts
- Harsha Charita by Bana describes King Harshavardhana’s royal camp near the Ajiravati (Rapti) River.
- Ancient texts mention the Rapti as a tributary of the Sarayu River, one of the five sacred rivers in Buddhist India.
Geographical Features of Rapti River
Origin and Course of Rapti
The Rapti River originates in the Middle Himalayas of Nepal, south of a prominent east-west ridgeline, between the western Dhaulagiri Himalaya and the Mahabharat Range, at an elevation of 3,048 meters. Initially, the river flows westward for nearly 100 km due to the Dundwa Range, a subrange of the Shiwalik Hills. After bypassing this natural barrier, it resumes its southward course towards the Ganga Basin.
The river has a total length of 600 km and enters Eastern Uttar Pradesh at Chanda Pargana, east of Kundwa village in Bahraich district. It then flows through Bahraich, Shravasti, Balrampur, Siddharthnagar, Sant Kabir Nagar, and Gorakhpur before joining the Ghaghara River near Barhaj in the Deoria district.
Major Locations Along the Rapti River
- Nepal – Originates in the Middle Himalayas.
- Chanda Pargana, Bahraich (Uttar Pradesh) – Entry point in India.
- Shravasti – Historically significant Buddhist site.
- Balrampur and Siddharthnagar – Agricultural regions dependent on the river.
- Gorakhpur – A major city affected by seasonal floods.
- Deoria – Confluence with the Ghaghara River.
Drainage Basin
The Rapti River Basin covers an area of 14,658 square kilometers, spanning Nepal and Uttar Pradesh, India. It is part of the Middle Ganga Plain, consisting of Himalayan foothills, the Terai region, and fertile alluvial plains.
Tributaries
Here are some major tributaries of Rapti:
- Burhi Rapti
- Banganga
- Suwawan Nala
- Rohini
- Ami
- Taraina
- Tura
- Bhakla
- Parasi
- Sikri
Floods and Environmental Concerns
The Rapti River is known for frequent flooding, particularly during the monsoon season (June–September). Due to heavy rainfall and sedimentation, the river often overflows, causing severe damage to agriculture, infrastructure, and human settlements.
Major Flood-Affected Areas:
- Gorakhpur
- Balrampur
- Shravasti
- Siddharthnagar
The Rapti Barrage, located upstream of Bhinga in Shravasti district, helps regulate floodwaters. It is managed by the State Government of Uttar Pradesh.
If you have any questions or want to share your thoughts about the Rapti River, feel free to leave a comment below. We’d love to hear from you!