Son River: Map, Origin, and Tributaries
Son River is a perennial river and the second-largest southern (right-bank) tributary of the Ganga River, which flows through multiple states in India. Originating near Amarkantak Hill, it flows through the states of Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar before merging with the Ganga River near Patna. A map of the Son River highlights its origin and course, along with its geographical features, tributaries, and dams.
Table of Contents
| River | Son |
| Length | 784 km |
| Originates at | Chhattisgarh |
| Join with | Ganga River |
| Catchment Area | 71,259 km² |
| Tributaries | Rihand, Johilla, Koel, etc. |
Geographical Features of Son River
Origin and Course
Son River originates near Pendra in the Gaurela-Pendra-Marwahi district of Chhattisgarh. It emerges from the Maikal Range of the Vindhya Hills, just east of the Narmada River’s source.
Flowing north-northwest, the river enters Madhya Pradesh and passes through Shahdol district. Upon reaching the Kaimur Range, it takes a sharp eastward turn, running parallel to the Kaimur Hills in an east-northeast direction through Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. Finally, it merges with the Ganga River west of Patna, covering a total length of 784 kilometers.
Major Cities Along the Son River
Several important cities and towns are situated along the river’s course, including:
- Arwal
- Daudnagar
- Deori
- Rohtasgarh
- Dehri
- Sonbhadra
- Maner
Map of River Son – Start to End
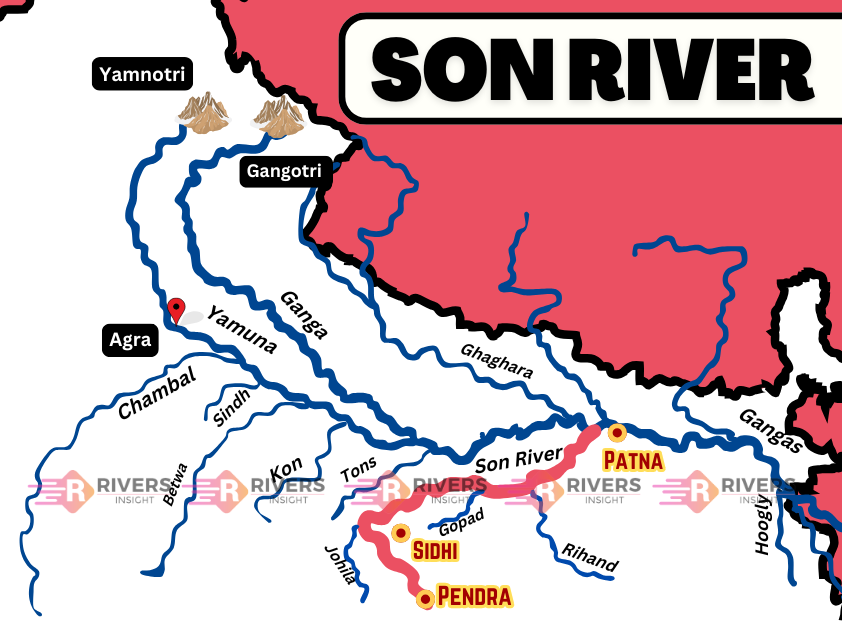
Catchment Area
The Son River basin covers a total catchment area of 71,259 km². It is enclosed by:
- North: Vindhya Range
- East: Punpun River system and Chotanagpur Plateau
- South: Baghelkhand Plateau and Mahadeva Hills
- West: Maikal and Bhamver Ranges
Tributaries of the Son River
Right-Bank Tributaries
- Johilla River
- Chhoti Mahanadi
- Gopad River
Left-Bank Tributaries
- Ghaghar River
- Rihand River
- Kanhar River
- North Koel River
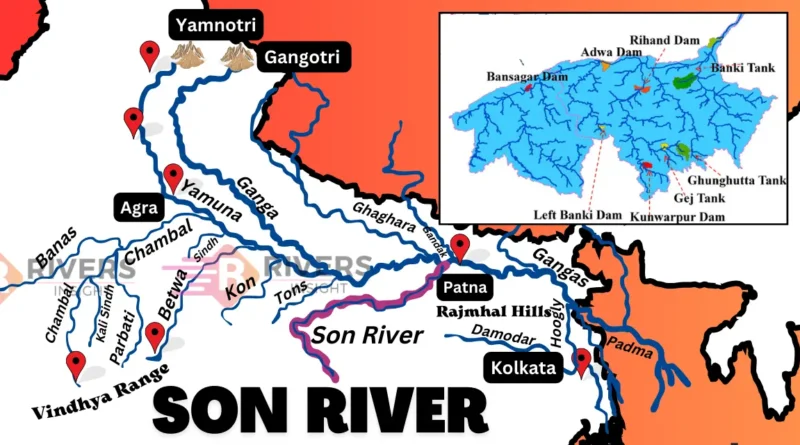
Dams and Hydroelectric Projects
- Bansagar Dam – Located in Madhya Pradesh, this multipurpose dam was completed in 2008.
- Rihand Dam –Rihand dam is situated in Uttar Pradesh on the Rihand River, this dam was built in 1962 to store water for irrigation and power generation.
- Indrapuri Barrage – Built in Bihar’s Rohtas district, spans over 1,400 meters and was completed in 1968. It is crucial for diverting water into the Sone Canal System.
Bridges
- Koilwar Bridge
- Nehru Setu
- Jawahar Setu
- Deolond Bridge
- Panduka Bridge
- Arwal-Sahar Bridge
So, this is all about the Son River. If you have any questions or want more information, feel free to comment below! Stay tuned to River Insight for more updates on India’s major rivers.

Very nice summary. Can you provide details of archaeological sites along the Sone River?