Ghaggar River: Overview with Map in India
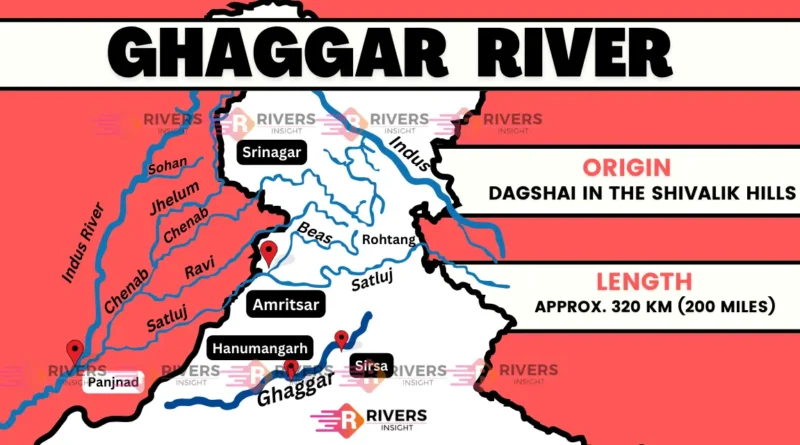
The Ghaggar River is a seasonal river in northern India and eastern Pakistan. It originates in the Sivalik Hills of Himachal Pradesh and flows through Haryana and Rajasthan before disappearing into the Thar Desert. The river flows from July to September during the monsoon season and dries up from October to March.
In this article, we will provide an in-depth analysis of the Ghaggar River, including detailed maps to illustrate its course, tributaries, and historical significance. We will also examine its water quality, the impact of human activities, and future conservation efforts.
Table of Contents
Physical Characterstics of Ghaggar River
The physical characteristics of Ghaggar River are as follows:
1. Length & Course of the Ghaggar River
The Ghaggar River flows for a total length of 320km before disappearing into the Thar Desert.
Its course can be divided into three main sections:
- Upper Course: The Ghaggar River originates in the Shivalik Hills of Himachal Pradesh, India, at an elevation of around 1,900 meters (6,200 ft) above sea level. The upper course of the river flows through a narrow valley, surrounded by steep hills and mountains. The river flows in a north-westerly direction, passing through the towns of Bilaspur and Ghumarwin.
- Middle Course: As the river enters the Indo-Gangetic Plain, it begins to flow in a south-westerly direction. The middle course of the river passes through the states of Punjab and Haryana, where it is joined by several tributaries, including the Kaushalya River and the Markanda River. The river flows through the cities of Patiala, Ambala, and Kurukshetra, before entering the state of Rajasthan.
- Lower Course: In Rajasthan, it flows through a dry and arid region, known as the Thar Desert. The lower course of the river is characterized by a gentle slope and a high water table. The river flows in a south-westerly direction, passing through the towns of Hanumangarh and Suratgarh, before disappearing into the desert.
2. Tributaries
The main tributaries of the Ghaggar River are:
- Kaushalya River
- Markanda River
- Sarsuti River
- Tangri River
- Chautang River
3. Drainage Basin
The Ghaggar River’s drainage basin covers an area of 29,524 km² (11,400 sq mi), with a dendritic drainage pattern. The basin spans across parts of Haryana, Rajasthan, and Punjab, and is home to a population of over 10 million people.
This seasonal river feeds two irrigation canals that extend into Rajasthan. The Hakra, which flows in Pakistan, is the continuation of the Ghaggar River in India, and they are together called the Ghaggar-Hakra River.
Historical Background of the Ghaggar River
The Ghaggar River has a rich and fascinating history that dates back thousands of years. This ancient river has played a significant role in the development of various civilizations in the Indian subcontinent.
Vedic Period: In the Vedic period (1500 BCE – 500 BCE), the Ghaggar River was considered a sacred river, mentioned in the Rigveda as the “Sarasvati“. It was believed to be a mighty river that flowed from the Himalayas to the Arabian Sea. The river was worshipped as a goddess and was considered the mother of all rivers.
Indus Valley Civilization: During the Indus Valley Civilization (3300 BCE – 1300 BCE), the Ghaggar was an important source of water for the people living in the region. The river supported the growth of several cities, including Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa, which were major urban centers of the civilization.
Also read: Indus River
Mahabharata and Puranas: In the Hindu epic, the Mahabharata, it River is mentioned as the site of the battle between the Pandavas and the Kauravas. The river is also mentioned in the Puranas, where it is described as a river that flows from the heavens to the earth.
Medieval Period: During the medieval period, the river continued to play an important role in the region’s economy and culture. The river supported agriculture, trade, and commerce, and several towns and cities flourished along its banks.
British Era: In the British era, the Ghaggar River was an important source of water for irrigation and other purposes. The British built several canals and dams to harness the river’s water, which led to the development of agriculture and industry in the region.